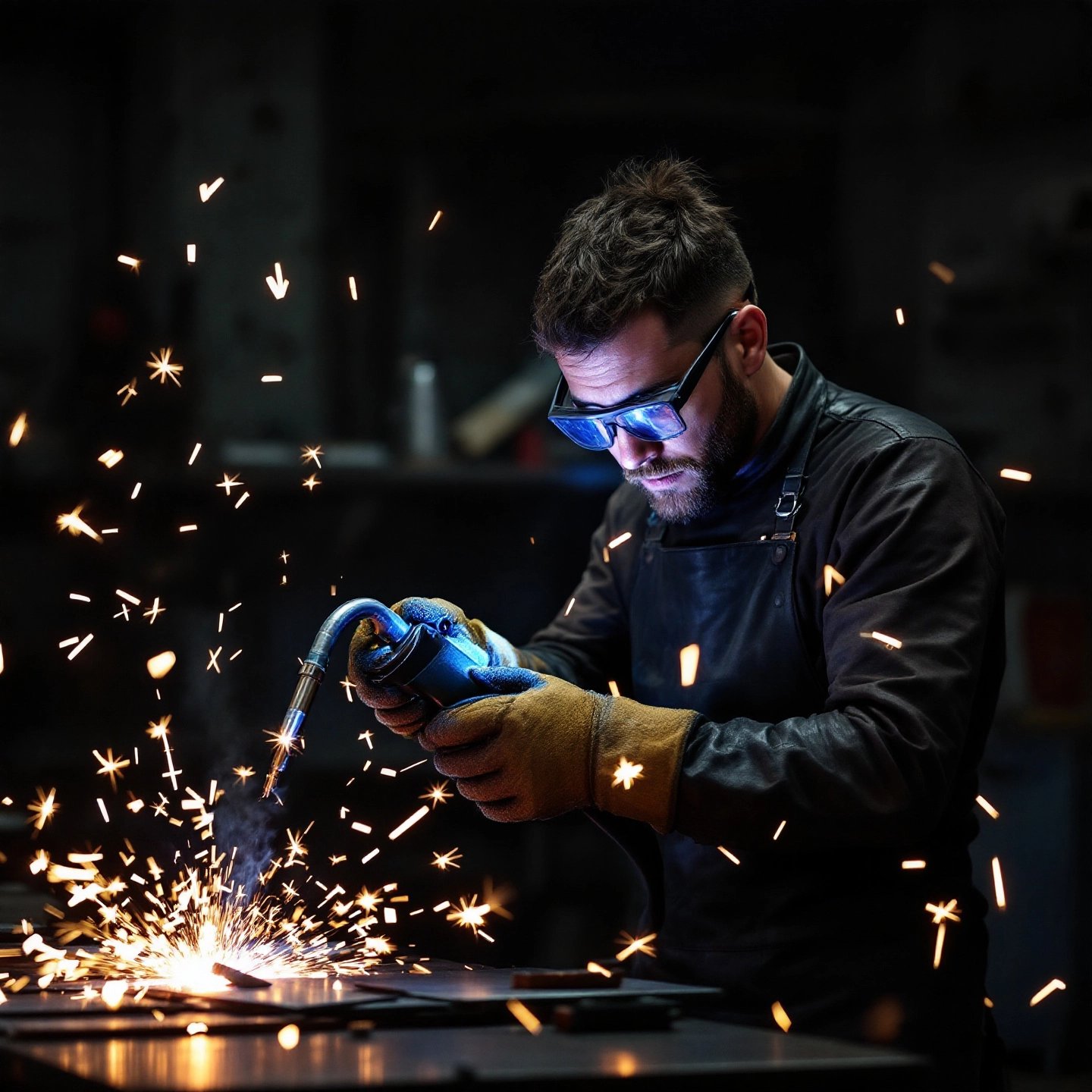

When it comes to metal fabrication, an aluminum welder plays a crucial role in joining aluminum components to create durable and functional structures. Aluminum welding is a specialized skill due to the unique properties of aluminum, which differ significantly from other metals like steel. This chapter will introduce you to the various aluminum welding processes, including MIG, TIG, stick, and spool gun methods, while shedding light on the challenges and solutions specific to welding aluminum, such as welding aluminum to steel .
Aluminum welding requires a deep understanding of the material's characteristics, including its softness, sensitivity, and the presence of an oxidized layer, which can complicate the welding process. These factors necessitate different techniques than those used for steel, making it vital for welders to familiarize themselves with the appropriate strategies and equipment.
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding is often favored for its speed and efficiency, particularly in industrial settings. It involves feeding a wire electrode through a welding gun, which creates an arc that melts the wire and base metal to form a weld. TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding , on the other hand, is renowned for its precision and the aesthetically pleasing results it produces, making it ideal for projects where the appearance of the weld is critical.
For those tackling smaller projects or repairs, stick welding and the use of a spool gun can offer practical solutions. Stick welding is known for its flexibility and ease of use without the need for shielding gas, while spool guns help maintain consistent wire feeding, crucial for achieving quality welds on aluminum.
Understanding these processes is essential not only for achieving strong and reliable welds but also for overcoming the unique challenges presented by aluminum. For instance, when welding aluminum to steel , special considerations must be made to address the differences in melting points and thermal conductivity.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide for both novice and seasoned welders, providing insights into the best practices and techniques for aluminum welding. Whether you're a beginner looking to grasp the basics or an experienced welder seeking to refine your skills, this roadmap will equip you with the knowledge needed to master the art of aluminum welding.
Aluminum is a metal with distinct characteristics that make it both advantageous and challenging to work with in welding applications. To achieve high weld quality , it's essential to understand these properties, such as its thermal conductivity, melting point, and the formation of oxide layers.
Aluminum's high thermal conductivity means it dissipates heat rapidly, which can be both a benefit and a hindrance in welding. This property requires precise control of heat input to prevent issues like burn-through, especially in thinner sections. Furthermore, aluminum's melting point is relatively low at 660°C (1220°F), compared to steel, which melts at around 1370°C (2500°F). This lower melting point necessitates careful attention to heat management during welding to avoid overheating and distortion.
Another critical factor is aluminum's tendency to form a thin oxide layer when exposed to air. This layer has a much higher melting point of 2072°C (3762°F) and can impede proper fusion if not removed prior to welding. Methods for removing this oxide layer include mechanical abrasion or chemical cleaning, ensuring a clean surface for welding.
| Property | Aluminum | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Melting Point | 660°C (1220°F) | 1370°C (2500°F) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Lower |
| Oxide Layer | Forms quickly, high melting point | Less significant |
These differences highlight why aluminum requires specialized techniques and equipment for welding. The question of 'can you weld aluminum?' is often answered with a resounding 'yes,' but it comes with the caveat that one must understand and adapt to these unique properties.
In terms of 'how to weld aluminum,' successful outcomes depend on choosing the right welding method, such as MIG or TIG, and adjusting parameters like amperage and travel speed to accommodate aluminum's characteristics. By mastering these techniques, welders can overcome the challenges posed by aluminum and achieve strong, durable welds.
As we delve deeper into the specific welding methods in the following sections, you'll gain a clearer understanding of how to effectively work with aluminum, ensuring high-quality results in your welding projects.
Before embarking on any aluminum welding project, it's vital to prioritize safety and preparation. Aluminum welding presents distinct challenges, such as the production of hazardous fumes and the need for meticulous cleaning to ensure quality welds. In this section, we'll explore the essential steps for safe welding and effective aluminum surface cleaning , answering the critical question of 'how do you weld aluminum?' with safety at the forefront.
Effective cleaning is a two-step process: removing oils and greases, by oxide removal. Here's how to do it:
By adhering to these safety measures and preparation steps, you ensure not only the quality of your welds but also the safety of your working environment. As we progress to specific welding techniques, remember that these foundational practices are key to mastering aluminum welding.
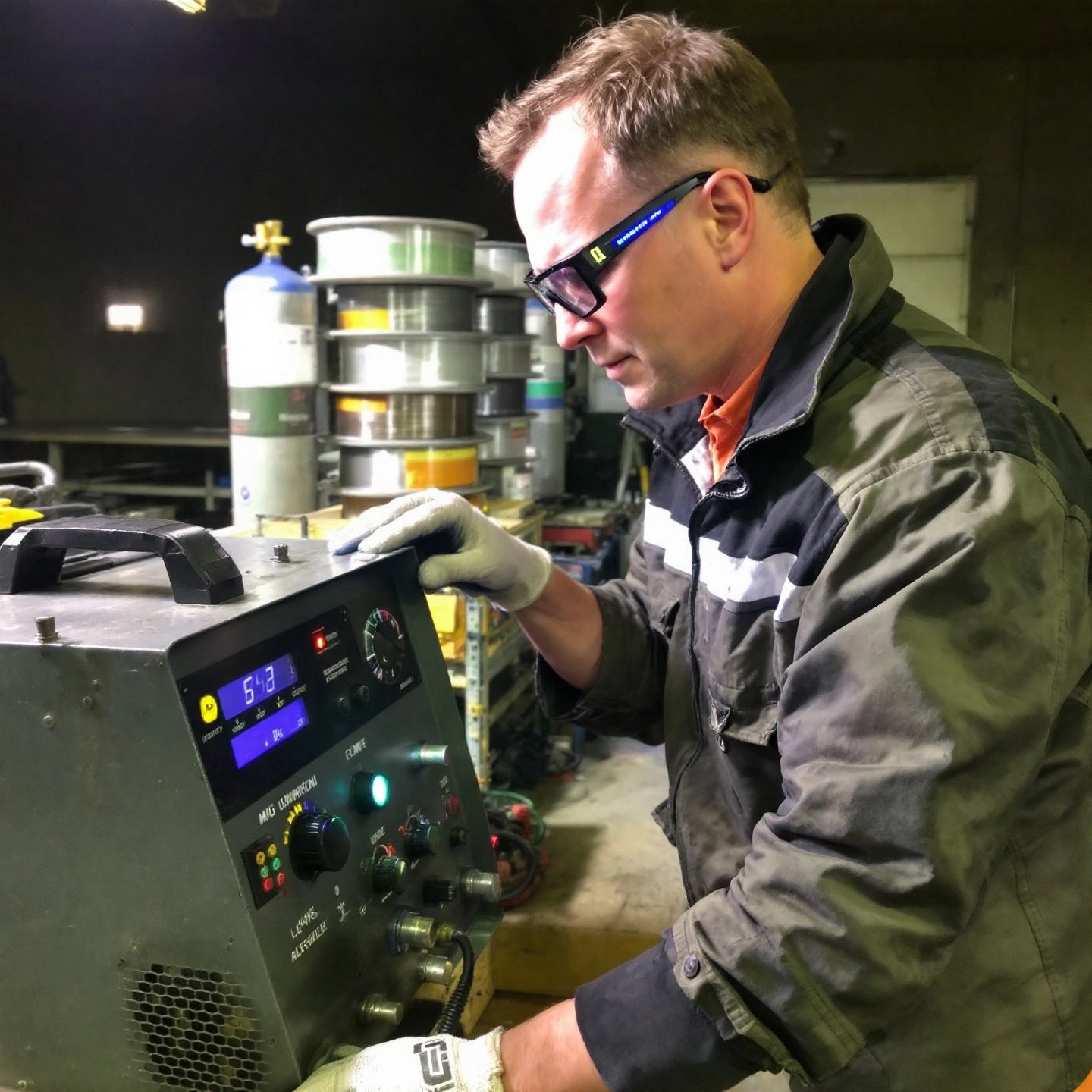

MIG welding aluminum presents unique challenges and opportunities, making it a preferred method for many welders due to its speed and efficiency. Understanding the nuances of MIG welding aluminum is crucial for achieving high-quality welds. This section will guide you through essential techniques, equipment settings, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Getting the correct settings on your MIG welder is vital. Start by selecting the appropriate wire. For general-purpose welding, ER4043 wire is recommended due to its versatility and resistance to cracking. For structural applications requiring higher tensile strength, ER5356 is suitable, though it demands careful handling to prevent cracking.
Next, focus on setting the correct voltage and amperage. Aluminum requires higher wire feed speeds and amperage compared to steel. Begin with a wire feed speed 30-100% higher than what you'd use for steel, adjusting based on your specific machine and project needs.
Shielding gas plays a pivotal role in protecting the weld pool from contamination. A 100% argon gas is standard, but an argon-helium mix can increase heat input and penetration for thicker materials. Avoid using CO2, as it reacts with aluminum and can impair weld quality.
Once your equipment is set, focus on technique. Aluminum's high thermal conductivity means you must weld quickly to prevent burn-through. Use a push technique with a 10-20 degree torch angle to ensure adequate gas coverage and minimize porosity.
Maintaining a proper tip-to-work distance, about 3/4 inch, is crucial. This distance helps control the arc and prevents the wire from burning back to the contact tip. Always aim for a spray transfer mode, which allows for a consistent arc and reduces spatter, enhancing weld quality.
Several issues can arise during MIG welding aluminum. Burn-through is common due to high heat input. To mitigate this, adjust your travel speed and practice on scrap pieces. Wire feed issues, such as bird-nesting, can be resolved by using a spool gun, which ensures consistent feeding.
When deciding between MIG and TIG welding, consider the project scope. MIG is typically faster and more suitable for larger projects where speed is essential, while TIG offers precision and is ideal for projects where aesthetics are a priority.
By mastering these strategies and understanding the intricacies of MIG welding aluminum, you can achieve robust and aesthetically pleasing welds. As we move forward, the next section will delve into TIG welding techniques, offering insights into achieving cleaner joints through precise control.
When it comes to achieving beautifully precise and clean welds, TIG welding aluminum stands out as a preferred method. Known for its precision and the aesthetic appeal of its welds, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) offers unparalleled control over the welding process, making it ideal for projects where quality and appearance are paramount.
To begin with, selecting the appropriate tungsten electrode is crucial. For aluminum, a pure tungsten or a 2% ceriated tungsten electrode is recommended due to its ability to maintain a stable arc. The electrode size should match the material thickness, typically around 1/16 to 3/32 inches for most applications. Setting up the TIG torch correctly is essential; ensure that the tungsten stick-out is no more than the diameter of the ceramic cup to maintain optimal gas coverage.
Shielding gas selection is another critical factor. Pure argon is the standard choice for GTAW welding aluminum , providing a stable arc and protecting the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. In cases where deeper penetration is needed, a helium-argon mix can be considered, although this requires adjustments in technique due to increased arc heat.
The use of a foot pedal in TIG welding allows for real-time control of the amperage, enabling precise adjustments to the heat input. This is particularly beneficial when working with aluminum, as it quickly dissipates heat, requiring constant modulation to avoid burn-through. By varying the pressure on the foot pedal, welders can seamlessly transition between different material thicknesses, ensuring a consistent weld bead.
Pulse settings are another tool in the TIG welder's arsenal, offering enhanced control over the arc. By adjusting the pulse frequency and background current, you can fine-tune the heat input, reducing the risk of distortion and improving weld penetration. A pulse frequency of 1-10 pulses per second is often effective for aluminum, helping to maintain a tight and focused arc.
Travel speed is equally important. Aluminum requires a faster travel speed compared to other metals to prevent excessive heat buildup. A steady hand and consistent pace are key; too slow, and you risk burn-through, too fast, and the weld may lack penetration. Practice on scrap pieces can help perfect this balance.
Achieving the desired 'stack of dimes' appearance in welds is a hallmark of skilled TIG welding. This is accomplished by rhythmically adding filler rod to the weld pool, ensuring each dab is consistent in size and spacing. Use a filler rod that matches or is slightly larger than the base material to ensure a strong bond.
By mastering these TIG welding techniques, you can create clean, precise welds that are both functional and visually appealing. As we continue, the next section will explore alternative methods like stick welding and spool gun usage, providing insights into their advantages for various project scales.
When it comes to welding aluminum, selecting the right method can significantly impact the efficiency and quality of your work. Two popular options are stick welding aluminum and using an aluminum spool gun . Each method offers unique advantages and is suited to different project scales and environments.
Stick welding, or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is a traditional method known for its versatility and simplicity. It's particularly favored for its ability to operate without the need for shielding gas, making it ideal for outdoor or less controlled environments. This method uses a consumable electrode coated in flux to create the weld, offering a robust solution for various metals, including aluminum.
Spool guns are designed specifically for feeding aluminum wire consistently, addressing one of the main challenges of MIG welding aluminum. The spool gun houses the wire closer to the weld site, reducing the risk of wire feed issues like bird-nesting, which can occur with traditional MIG setups.
When deciding between stick welding and using a spool gun, consider the scale and environment of your project. For smaller, on-site repairs or projects in challenging conditions, stick welding offers unmatched convenience and adaptability. However, for larger-scale industrial applications where consistent quality and speed are paramount, a spool gun provides the precision and reliability needed to achieve superior results.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, you can select the best tool for your specific needs, ensuring efficient and high-quality aluminum welding. As we proceed, the next section will guide you through selecting the right consumables and fillers, integral to achieving the best possible welds.
When it comes to achieving high-quality welds, the choice of consumables and fillers is crucial. The right selection can make or break the success of your aluminum welding project. This section will guide you through the essential considerations for choosing aluminum welding rods and aluminum welding wire , as well as adhesives like JB Weld aluminum, ensuring you achieve optimal results.
Choosing the right filler material depends on the specific requirements of your project. Aluminum filler rods and wires are categorized by their alloy series, each offering distinct properties:
| Filler Alloy | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 4043 | Good fluidity, crack-resistant | General-purpose welding, 6XXX series alloys |
| 5356 | Higher strength, good corrosion resistance | Marine applications, 5XXX and 6XXX series alloys |
| 5554 | Low magnesium content, good for elevated temperatures | Welding 5XXX series alloys like 5052 |
For projects where aesthetics are important, such as those requiring anodizing, 5XXX series fillers are preferred due to their color match. Conversely, 4XXX series fillers like 4043 are ideal for applications where fluidity and crack resistance are priorities, especially when welding 6XXX series alloys.
In addition to welding, adhesives like JB Weld aluminum offer alternative solutions for joining aluminum components, particularly in applications where welding is impractical. These adhesives provide strong bonds and can be used for repairs or as supplemental joining methods in less critical areas.
When selecting aluminum profiles and customized extrusions, consider the high-quality offerings from Shengxin Aluminum. As a leading manufacturer, Shengxin provides a wide range of aluminum products that can be tailored to meet specific project needs. Their extensive production capabilities ensure precision and performance, making them a reliable choice for both standard and specialized applications.
By carefully selecting the right consumables and fillers, and leveraging resources like Shengxin Aluminum’s profiles, you can enhance the quality and durability of your aluminum welds. As we continue, the next section will address common mistakes and effective troubleshooting strategies, equipping you with the knowledge to overcome potential challenges in your welding projects.
Welding aluminum can present numerous challenges, even for seasoned professionals. Understanding common welding mistakes and effective troubleshooting techniques is essential for achieving high-quality welds. This section will identify frequent errors such as porosity, cracking, and incomplete fusion, providing step-by-step solutions to overcome these issues.
Both MIG and TIG welding have unique challenges that require specific troubleshooting techniques:
By mastering these troubleshooting techniques, you can significantly improve your welding outcomes, ensuring strong and reliable aluminum welds. As we move forward, the next section will offer insights into finding local aluminum welding services, helping you evaluate their expertise for your specific project needs.

Finding the right aluminum welder near me can be a daunting task, especially when you want to ensure the highest quality for your project. Whether you're embarking on a small repair or a large-scale construction, selecting a local welding service that matches your needs is crucial. Here, we'll explore key factors to consider when evaluating local welding experts, ensuring you make an informed decision.
When searching for local welding services , start by assessing the expertise and experience of potential service providers. Look for companies that specialize in aluminum welding and have a proven track record of handling projects similar to yours. Experienced welders will not only have the technical skills needed but also the practical knowledge to overcome common challenges associated with aluminum welding.
Advanced equipment and modern techniques are indicators of a professional welding service. Companies that invest in the latest welding technology are often able to deliver superior results, with precision and efficiency.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring your project requirements are met. Choose a service provider that prioritizes customer satisfaction and is willing to listen and respond to your needs.
For projects requiring high-quality aluminum profiles or customized extrusions, consider the extensive offerings from Shengxin Aluminum . With a wide range of products and advanced production capabilities, Shengxin Aluminum is well-equipped to support large-scale and specialized projects with precision and reliability.
By following these guidelines, you can find a local aluminum welding service that meets your specific needs, ensuring a successful outcome for your project. As we conclude, the next section will recap the key lessons learned and encourage continuous learning in the field of aluminum welding.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on mastering aluminum welding , it's clear that the journey from preparation to execution in aluminum welding is both challenging and rewarding. We've explored essential preparation steps, delved into the intricacies of MIG and TIG welding techniques, and highlighted the importance of selecting the right consumables and fillers. Each of these components plays a vital role in achieving high-quality welds, ensuring both safety and efficiency in your projects.
The importance of thorough preparation cannot be overstated. Ensuring a clean, safe workspace and understanding the unique properties of aluminum set the foundation for successful welding. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned welder, adhering to these preparatory steps is crucial for avoiding common pitfalls and enhancing weld quality.
Our deep dive into MIG and TIG welding strategies showcased the nuanced approaches required for each method. From mastering equipment settings and wire selection in MIG welding to the precision control offered by TIG welding, these techniques are pivotal in crafting strong, aesthetically pleasing welds. Understanding when to use each method based on project requirements is a skill that will serve you well in diverse welding scenarios.
Moreover, we've addressed common mistakes and provided troubleshooting tips to guide you through the inevitable challenges that arise in aluminum welding. By recognizing and correcting errors like porosity and incomplete fusion, you can improve your outcomes and build confidence in your welding capabilities.
Looking ahead, the future of aluminum welding is bright, with advancements in advanced aluminum fabrication offering new possibilities. Embracing technologies like AI and automation, as discussed in our references, can lead to more efficient, sustainable, and precise aluminum fabrication processes. These innovations promise to transform the industry, making it more accessible and efficient for welders worldwide.
In conclusion, continuous learning and experimentation are key to staying ahead in the ever-evolving field of aluminum welding. By applying the knowledge gained from this guide, you'll be well-equipped to tackle any welding project with confidence and precision. The future holds endless possibilities for those willing to adapt and innovate, paving the way for exciting advancements in aluminum fabrication.
TIG welding is often considered the best for aluminum due to its precision and control, but MIG welding is faster and suitable for larger projects.
Yes, aluminum requires welders with specific capabilities like pulse settings for MIG or AC/DC options for TIG to handle its unique properties.
A TIG welder is ideal for precision, while a MIG welder with a spool gun is great for speed and efficiency on larger projects.
Look for local services with specialized experience in aluminum welding, check references, and evaluate their equipment and techniques.
Avoid porosity by ensuring clean surfaces and proper gas flow, and prevent cracking with correct joint preparation and heat management.
 Интернет Сервис
Интернет Сервис 0086 136 3563 2360
0086 136 3563 2360 sales@sxalu.com
sales@sxalu.com +86 136 3563 2360
+86 136 3563 2360